In today’s fast-paced retail and e-commerce environment, effective inventory management is more crucial than ever. Companies must be able to track their products accurately, manage stock levels efficiently, and facilitate seamless sales processes. This is where SKU (Stock Keeping Unit) and UPC (Universal Product Code) come into play. While both serve essential roles in product identification, they have distinct differences that can impact how businesses operate.
In this article, we will delve deep into the definitions of SKU and UPC, their unique features, and benefits, and how they complement each other in the realm of inventory management. Additionally, we will explore how VVAP Global, a leader in logistics and supply chain management, can help businesses implement and optimize their SKU and UPC systems for maximum efficiency.
What is an SKU?
A Stock Keeping Unit (SKU) is a unique identifier assigned to products by a company for internal tracking and inventory management purposes. Unlike standardized codes, SKUs are tailored to reflect a company’s specific needs and product attributes, such as color, size, or category.
Key Characteristics of SKUs:
Customization: Each SKU is created by the business, allowing for flexibility in its structure. For instance, a clothing retailer might create an SKU such as “TSHIRT-RED-LG” to denote a large red t-shirt.
Alphanumeric Codes: SKUs can include letters and numbers, enabling businesses to encode information about the product within the SKU itself.
Internal Use: SKUs are primarily used within a company’s inventory management system and are not standardized across the industry.
Benefits of Using SKUs:
Enhanced Inventory Management: By using SKUs, businesses can monitor stock levels, identify slow-moving products, and make informed restocking decisions. This leads to better inventory turnover and reduced holding costs.
Streamlined Order Fulfillment: SKUs facilitate organized picking and packing processes. When an order is received, employees can quickly locate the SKU in the inventory system, reducing errors and time spent fulfilling orders.
Data-Driven Insights: Analyzing sales data by SKU allows companies to identify trends, track product performance, and develop targeted marketing strategies.
Customizability: Businesses can structure their SKUs based on product features that matter most to them, allowing for a tailored approach to inventory management.
What is an SKU?
A Stock Keeping Unit (SKU) is a unique identifier assigned to products by a company for internal tracking and inventory management purposes. Unlike standardized codes, SKUs are tailored to reflect a company’s specific needs and product attributes, such as color, size, or category.
Key Characteristics of SKUs:
Customization: Each SKU is created by the business, allowing for flexibility in its structure. For instance, a clothing retailer might create an SKU such as “TSHIRT-RED-LG” to denote a large red t-shirt.
Alphanumeric Codes: SKUs can include letters and numbers, enabling businesses to encode information about the product within the SKU itself.
Internal Use: SKUs are primarily used within a company’s inventory management system and are not standardized across the industry.
Benefits of Using SKUs:
Enhanced Inventory Management: By using SKUs, businesses can monitor stock levels, identify slow-moving products, and make informed restocking decisions. This leads to better inventory turnover and reduced holding costs.
Streamlined Order Fulfillment: SKUs facilitate organized picking and packing processes. When an order is received, employees can quickly locate the SKU in the inventory system, reducing errors and time spent fulfilling orders.
Data-Driven Insights: Analyzing sales data by SKU allows companies to identify trends, track product performance, and develop targeted marketing strategies.
Customizability: Businesses can structure their SKUs based on product features that matter most to them, allowing for a tailored approach to inventory management.
What is a UPC?
A Universal Product Code (UPC) is a standardized barcode that consists of 12 numerical digits. It is widely used in retail environments to identify products at the point of sale. The UPC is issued and regulated by GS1, a global standards organization that ensures consistency across industries and countries.
Key Characteristics of UPCs:
Standardization: UPCs are uniform across all retailers, meaning that a specific product will always have the same UPC, regardless of where it is sold.
Numeric-Only Format: UPCs consist solely of digits, making them simpler and quicker to scan using barcode scanners at checkout.
External Use: Unlike SKUs, UPCs are designed for universal application, allowing retailers, suppliers, and distributors to recognize products easily.
Benefits of Using UPCs:
Efficient Sales Transactions: UPCs streamline the checkout process by enabling quick and accurate scanning of products, reducing wait times for customers.
Global Recognition: Since UPCs are standardized, they facilitate product sales in various markets, allowing businesses to expand internationally without re-labeling products.
Retail Compliance: Many retailers require UPCs for inventory tracking, making them essential for suppliers looking to partner with major retail chains.
Consistent Product Tracking: UPCs provide a reliable way to track products from manufacturing to sale, ensuring that all parties involved in the supply chain can access the same product information.
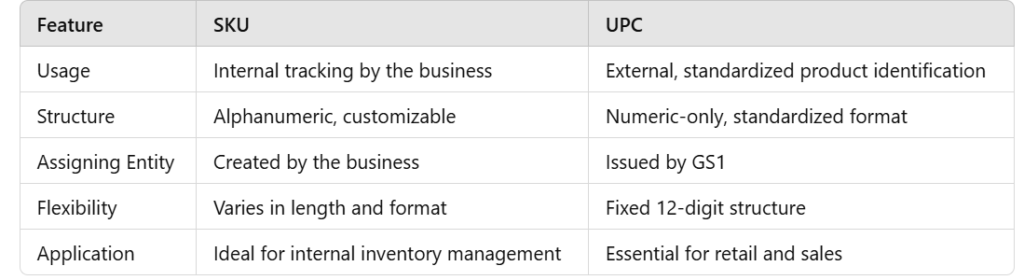
Key Differences Between SKU and UPC
While SKUs and UPCs both serve as identifiers for products, they have distinct differences that influence their applications in inventory management:
Why Businesses Need Both SKU and UPC
The complementary roles of SKUs and UPCs make them both necessary for effective inventory management. Here’s why:
Comprehensive Tracking: While SKUs offer detailed internal tracking tailored to specific business needs, UPCs provide a standardized method for identifying products across the global marketplace.
Improved Operational Efficiency: Using both SKUs and UPCs enhances operational efficiency by streamlining processes from the warehouse to the sales floor.
Data Analysis and Insights: Businesses can analyze sales and inventory data by SKU for internal decision-making while relying on UPCs for external reporting and compliance.
Facilitation of E-commerce: For e-commerce businesses, SKUs help in managing online inventory, while UPCs ensure compliance when products are sold through various channels.
How VVAP Global Can Help with SKU and UPC Management
VVAP Global specializes in logistics and supply chain management, providing comprehensive services to optimize inventory tracking and product management through effective SKU and UPC systems. Here are some ways VVAP Global can assist businesses:
Inventory Organization: VVAP Global can help businesses establish a well-structured SKU system tailored to their product lines. By analyzing product attributes, VVAP Global can design SKUs that enhance inventory management.
Barcode Solutions: For companies needing UPCs, VVAP Global offers barcode generation services and guidance on obtaining UPCs from GS1. This ensures that products are ready for retail compliance and global sales.
System Integration: VVAP Global provides expertise in integrating SKUs and UPCs with clients’ ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and POS (Point of Sale) systems. This synchronization improves cross-departmental collaboration and data accuracy.
Global Logistics Support: With extensive experience in international shipping, VVAP Global uses UPCs to streamline customs processing, ensuring products move smoothly across borders.
Consultation and Training: VVAP Global offers consultation services to educate businesses about best practices for SKU and UPC management, helping them optimize their systems for better results.
Tailored Software Solutions: VVAP Global can provide or recommend software that automates the tracking and management of SKUs and UPCs, ensuring that businesses have real-time visibility into their inventory levels and product status. This software can also generate reports that help in strategic decision-making.
Analytics and Reporting: By leveraging data analytics, VVAP Global helps businesses understand their inventory performance better. With insights from SKU and UPC data, companies can identify which products are performing well and which are not, enabling better purchasing and marketing strategies.
Real-World Applications: How VVAP Global Supports Various Industries
VVAP Global’s expertise in SKU and UPC management is beneficial across various industries. Here’s how different sectors can leverage these codes effectively:
E-commerce Businesses: For e-commerce platforms, managing inventory through SKUs allows for precise order fulfillment. VVAP Global aids in creating an efficient SKU structure that enhances stock visibility. Additionally, UPCs ensure compliance when products are listed on retail marketplaces.
Manufacturers and Suppliers: Manufacturers can benefit from custom SKU systems that reflect their diverse product lines. VVAP Global helps in obtaining UPCs to facilitate distribution to retailers and wholesalers, ensuring products are easily identifiable.
Retailers and Wholesalers: Retailers often require UPCs for inventory management, making it essential for wholesalers to have UPCs for their products. VVAP Global assists in generating and integrating these codes, enabling smooth operations between suppliers and retailers.
Health and Wellness Products: In the health sector, where product integrity and accurate tracking are critical, VVAP Global can provide tailored SKU management solutions that comply with regulations, ensuring that businesses maintain the highest standards for their products.
Consumer Electronics: With rapid changes in technology, consumer electronics companies must manage their inventory carefully. VVAP Global helps in creating SKUs that reflect product specifications while providing UPCs for easy recognition in retail environments.
Tips for Choosing and Implementing SKUs and UPCs
Implementing SKUs and UPCs effectively requires careful planning. Here are some tips:
Designing Effective SKUs: Consider using a consistent format that includes key product attributes (e.g., product type, color, size) to make SKUs intuitive and informative.
Choosing a UPC Provider: Partner with a reliable organization, such as GS1, to obtain UPCs. Ensure that the UPCs are registered correctly to avoid conflicts in product identification.
Maintaining Consistency: Regularly review and update SKU and UPC systems to reflect any changes in product offerings or inventory practices.
Training Employees: Provide training to staff on how to use SKUs and UPCs effectively, emphasizing their importance in inventory management and sales processes.
Utilizing Technology: Leverage software solutions that integrate SKU and UPC management with inventory systems to automate tracking and improve accuracy.
Conducting Regular Audits: Regular audits of your SKU and UPC systems can help identify discrepancies and ensure that inventory records are accurate. This practice can prevent stockouts and overstock situations.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between SKU and UPC is vital for effective inventory management and operational efficiency. By utilizing both, businesses can optimize their inventory processes and enhance product tracking, leading to better sales and customer satisfaction.
VVAP Global stands ready to assist businesses in navigating the complexities of SKU and UPC management. With tailored solutions, expert guidance, and innovative technology, VVAP Global can help streamline your inventory processes and enhance your supply chain efficiency. Whether you’re a small e-commerce startup or a large manufacturer, VVAP Global has the expertise to elevate your business.